First Version: Single-Machine "HA" Homelab (Initial Project)
Full English translation coming soon.
Introduction
This page describes the initial project I had planned to experiment with Kubernetes. This project evolved into a different final decision: a 3-node Proxmox cluster (see 3-Node Proxmox Cluster).
The initial idea was to create a transitional step toward a complete distributed infrastructure, experimenting with Kubernetes (K3S), Infrastructure as Code (OpenTofu/Terraform), Git, and CI/CD pipelines, while remaining on a single physical machine.
Objectives
Practical Learning
This single-machine infrastructure allows acquiring hands-on experience with:
- Kubernetes (K3S): Installation, configuration, and management
- Infrastructure as Code: OpenTofu/Terraform for declarative infrastructure
- GitOps and CI/CD: Automated deployments with Forgejo Actions
- Observability: Prometheus, Grafana, Loki stack
Network Architecture
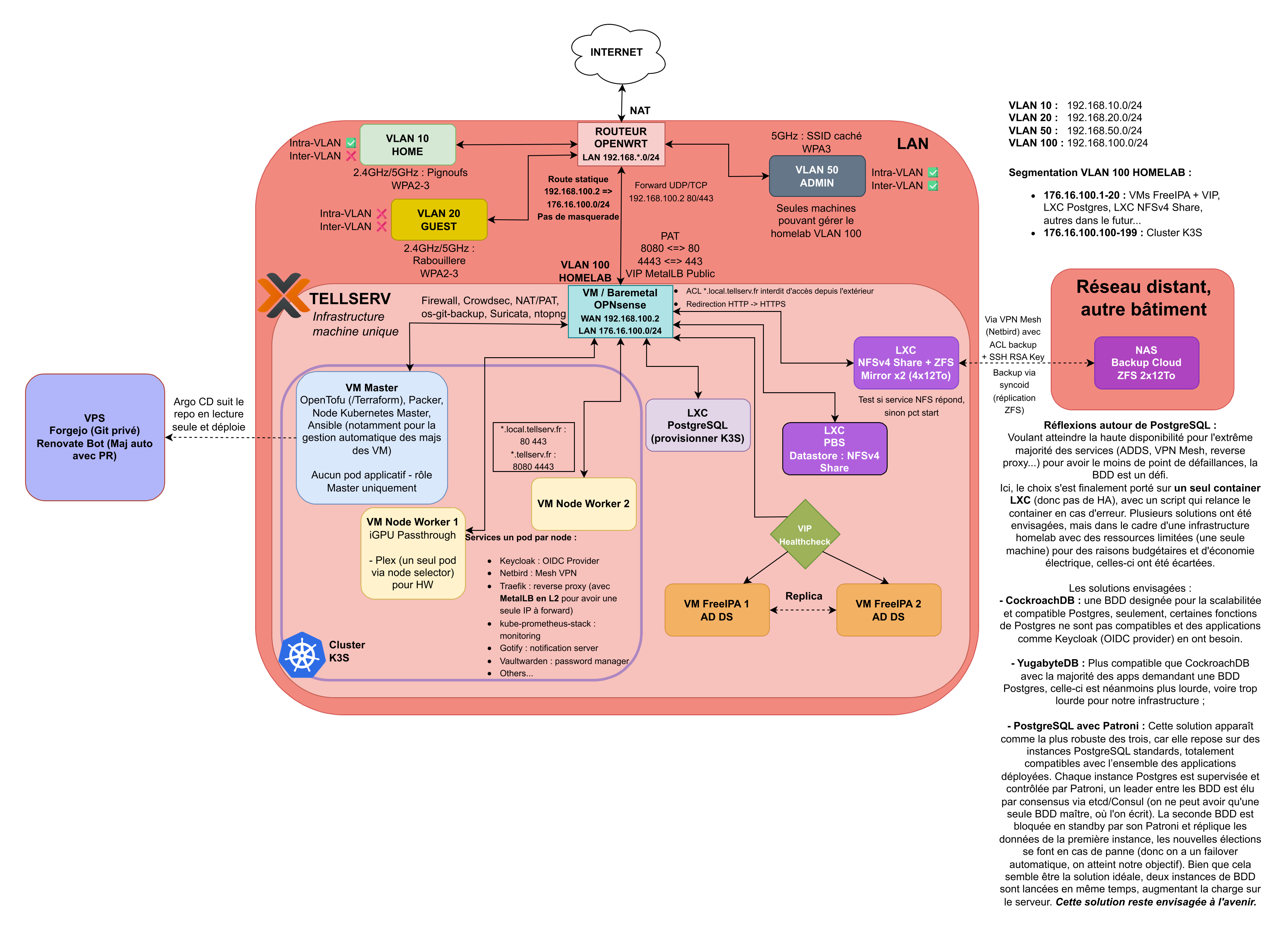
What Can Be Learned
This single-machine infrastructure allows acquiring essential skills:
- Kubernetes deployments and management
- DevOps practices (IaC, GitOps, CI/CD)
- Monitoring and logging
- Automation with Ansible and OpenTofu
Limitations of This Approach
1. No Real High Availability (HA)
Main limitation: With a single machine, there is no redundancy:
- Single point of failure (SPOF)
- Maintenance requires downtime
- No automatic failover
2. Distributed Storage Impossible to Test
Critical limitation: Distributed storage (Ceph, Linstor DRBD, Longhorn with replication) requires at least 3 nodes:
- Ceph: Requires 3 nodes minimum (ideally 5+) for quorum and replication
- Linstor DRBD: Needs multiple nodes for synchronous data replication
- Longhorn (replication): Cannot replicate data to other nodes
3. Limited Scalability
- Cannot add worker nodes to increase capacity
- Hardware limitations of single machine
- No experience with horizontal auto-scaling
4. Simplified Network
- All pods on the same physical machine
- Negligible network latency
- No multi-node CNI complexity
5. No Realistic Failure Simulation
- Cannot simulate node failure
- No automatic failover testing
- No disaster recovery validation
Why Start with Single Machine?
Despite limitations, this approach has significant advantages:
1. Cost and Simplicity
- Reduced investment (no need to buy 3-5 servers immediately)
- Lower power consumption
- Simplified maintenance
2. Progressive Learning Curve
- Manageable complexity
- Simplified debugging
- Less costly mistakes
3. Architecture Validation
- Test which services work well on K8S
- Optimize resource configurations
- Identify incompatibilities before scaling
4. Preparation for Evolution
This version serves as a foundation for the complete cluster:
- Reusable IaC code
- Tested and validated Kubernetes manifests
- Operational CI/CD pipelines
Evolution Toward Real Cluster (Initial Plan)
If this version had been implemented and stabilized, evolution toward multi-node cluster would have been natural:
Minimum for functional HA cluster:
- 3 nodes (1 control plane + 2 workers, or 3 mixed nodes)
- Gigabit network switch
- Distributed storage (Ceph ideally requires 5 nodes)
Planned migration strategy:
- Add second node to form a cluster
- Test pod distribution between nodes
- Add third node for quorum and enable HA (or use a Qdevice)
- Deploy Ceph or Linstor for distributed storage
- Migrate critical workloads with replication
Conclusion and Evolution to 3-Node Cluster
This initial single-machine "HA" homelab project was an important reflection in the evolution of my infrastructure:
Positive points of initial reflection:
- Clear identification of Kubernetes learning objectives
- Architecture and target configuration validation
- Understanding of single-machine approach limitations
Final decision: After analyzing the limitations, particularly the impossibility to test distributed aspects (high availability, Ceph storage, load distribution), I decided to opt directly for a 3-node Proxmox cluster.
This decision allows:
- Experimenting with real K3S VMs distributed across physical production nodes
- Testing high availability and distributed storage (Ceph)
- Learning complex networking aspects of a real cluster
- Building a solid foundation for production-ready infrastructure
For more details on the final architecture, see the 3-Node Proxmox Cluster page.
Detailed English translation of this page is in progress.